How D2D communication in 5G era can transform our connected world
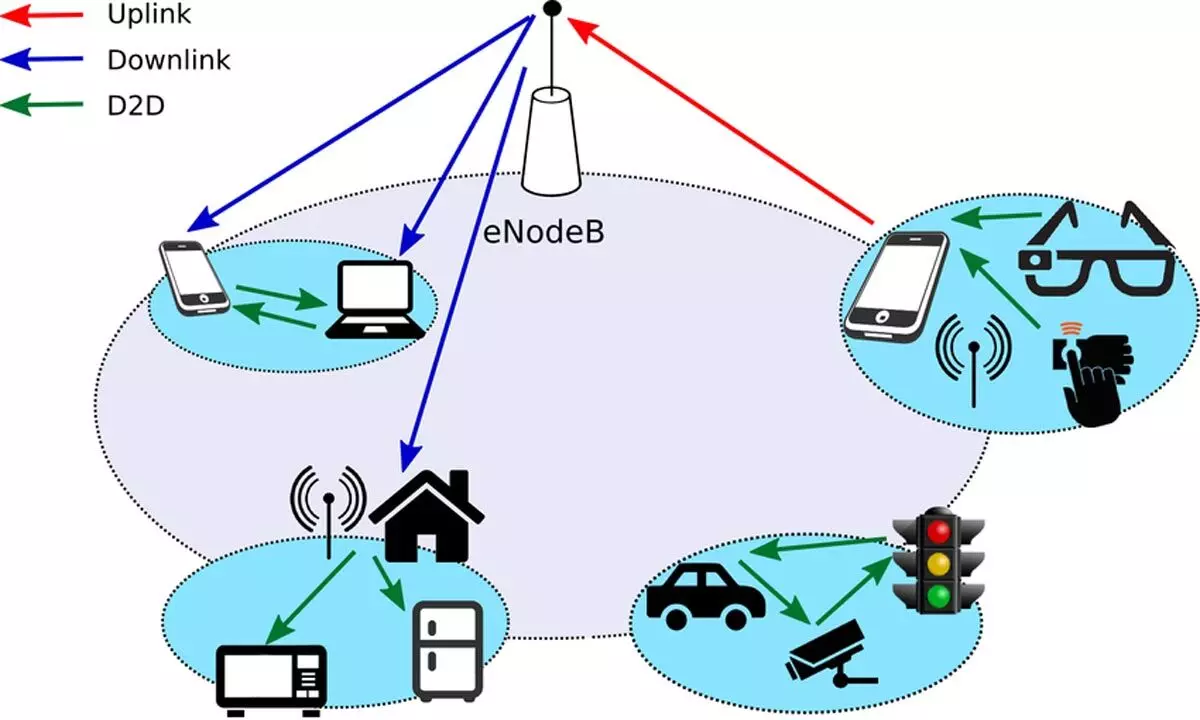
Device-to-device (D2D) communication is a technology that allows communication among devices without the involvement or with only partial involvement of a base station
image for illustrative purpose
D2D communication is an important aspect in 5G networks. 5G supports connectivity among a large number of devices. Growth in the number of devices requires a large number of spectrum resources to support a variety of applications and causes burden on the base station. D2D communication skips the need to forward data to the base station from the device and helps the devices to take part in direct peer to peer (P2P) transmission. It is expected that D2D will continue to evolve in future releases of the 3gpp standards
The recently approved 3gpp (3rd Generation Partnership Project) release 18 package includes work on embracing AI, ML in the evolution of 5G advanced, enhancements in network energy savings, coverage and mobility, MIMO (Multi Input Multi Output) evolution, MBS (Multicast and Broadcast Service) and positioning. It will enable more flexible and efficient spectrum use for 5G deployment and support Extended Reality (ER), cloud gaming devices, low complexity UEs (User Equipments), vehicular devices and Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs). Release 18 will enable flexible network topology by exploiting diverse nodes such as IAB (Integrated Access and Backhaul) nodes, RF repeaters and relays and integration with NTNs (Non Terrestrial Networks). The author's article on NTNs is already published in this paper.
5G advanced continues to enhance direct communication between users or users and infrastructure. Sidelink or Device-to-Device (UE-to-UE) relay allows users to receive information from networks via other users. In this article this 5G advanced technology is discussed.
The Device to Device communication (D2D) also known as Sidelink or Proximity Services (ProSe) has been defined in the LTE Advanced (3GPP Rel 12) in 2015 and is evolving. D2D communication is a technology that allows communication between devices without the involvement or with only partial involvement of a base station. The D2D communication can be used in the following three scenarios:
1. In coverage: Both the UEs which have to communicate are in cell coverage area
2. Partial coverage: one UE is in cell coverage area and the other is not
3. Out of coverage: Both the UEs are in out of cell coverage area.
The advantages in D2D communication are:
1. Increase of spectral efficiency: Instead of using two radio channels, one between UE1 and base station and the other between UE2 and base station, only the radio channel between UE1 and UE2 is used.
2. Increase of system capacity: System capacity increases due to sharing the spectrum resources between cellular users and D2D users.
3. Reduction in network latency, because of direct communication between devices. D2D will be one of the necessary features to support real time services in future 5G systems.
4. Less power consumption by UE: Transmission power required by UE1 to reach the adjacent UE2 will be less than that required to reach the base station.
5. Expansion of network coverage through Relay mode: A UE, say X, at the cell edge may encounter poor signal quality while connecting to the base station. At the same time another UE, say Y, close to it that has a better signal to reach the base station may act as a relay for X. Thus D2D link X-Y followed by cellular link Y- Base station connects X to the base station.
6. Better connectivity: Signal quality to the adjacent device may be better compared to the signal quality to base station.
7. Provides higher data rates and higher bandwidth: Due to the close proximity to the adjacent device and potentially favourable propagation conditions between the devices, higher data rates and higher bandwidth are possible.
8. Better QOS (one link instead of two)
9. Reliability increases with D2D link acting as diversity to regular cell connectivity.
10. D2D communication offers local management of short distance links and allows separation of local traffic from global traffic (local traffic offloading). This will remove the load burden on the backhaul and core network caused by data transfer and related signalling for local traffic and also reduce the effort to manage the local traffic at Central network nodes.
11. Content privacy and anonymity because central storage is not involved for storing the shared information between the devices.
Uses of D2D communication
1. Public Safety: The main use case of D2D communication is in public safety networks. D2D communication will be able to assist in the mitigation and evacuation in the event of disaster. Even though the cellular network has gone down, some UEs which are active can communicate with each other.
2. Commercial/advertisements: When someone is walking in a commercial street, advertisements can be received by him/her from nearby stores after discovering him/her..
3. Social networks: When someone has gone out, a nearby friend can discover and communicate to him/her.
4. Vehicular (V2X) communication: V2X means vehicle to everything (Vehicle to vehicle or Vehicle to Infrastructure or Vehicle to person). This requires stringent QOS requirements. V2X can find application in vehicle platooning. If the vehicles are moving in a cross country where signal from the base station is poor, the vehicles can communicate with one another to avoid collision using this technology.
5. Rural network improvement: In rural areas, subscribers will be less and their communities of interest will be mostly within the village itself. D2D technology is suitable for this scenario.
6. IOT devices with a very long expected battery life time will benefit from short D2D links.
Technical requirements
- Device discovery: One mode can be, a device can send the signal 'I am here' and whichever device can receive that signal, it is in the vicinity of that device and can carry out D2D communication.
- Resource allocation: Time, frequency resources between devices and for the ongoing cellular network has to be efficiently managed and this aspect is very crucial for D2D communications
- Mobility management: The devices may be moving and so doppler shift and frequency offset have to be managed and also there may be break in communication.
- Synchronisation: Timing, frequency synchronisation between devices has to be ensured.
- Coexistence (licensed and unlicensed bands): Frequency and timing resources of side links and 5G NR have to be shared (for example through Dynamic Spectrum Sharing technique)
- Security, privacy and lawful interception
D2D has evolved from Release 12 to Release 17. Let us analyse this evolution:
D2D in Release 12: Release 12 supports Proximity Services. New PC5 interface is defined for the exchange of data between UEs. This interface bypasses the base station and so improves spectral efficiency. Two modes are defined for resource allocation:
- Mode1: when the UEs are in-coverage, the resources are scheduled by the base station.
- Mode 2: when the UEs are out of coverage, the resources are allotted in random fashion/ preconfigured fashion.
Two channels are defined to enable resource allocation:
- Physical Sidelink Control Channel (PSCCH): It contains Sidelink Control Information and is transmitted twice to increase the detection probability.
- Physical Sidelink Shared Channel (PSSCH): It contains data and is transmitted four times to increase the reliability. This multiple transmission is called Open-loop HARQ (Hybrid Automatic Repeat Request) transmission.
There is no acknowledgement for Sidelink channels.
D2D in Release 14: In this Release, enhancements for Cellular Vehicle to everything communications (C-V2X) are supported. Two more modes of Resources Allocation are defined:
- Mode 3: for the in coverage scenario, scheduling by base station and this mode accommodate high Doppler for vehicles moving in opposite directions and for high vehicle density.
- Mode 4: for the out of coverage scenario, with distributed scheduling, resources allocation is Spectrum Sensing based semi- persistent scheduling to reduce collisions due to transmissions at the same time.
In Release 14, PSCCH and PSSCH are separated in frequency and not in time as in Release 12.
D2D in Release 16 (5G NR)
Release 16 focussed on V2X. The 5G NR advantages (wide bandwidth, multiple frequency bands, flexible frame structure (numerology), shorter Transmission Time Intervals (TTIs), massive MIMO support, advanced modulation and coding schemes) are exploited to enhance reliability, improvement of spectral efficiency and reduction of latency in C-V2X communications. The key specifications are:
- Peak data rate: 25 mbps to 1gbps
- Latency: 5 ms to 100 ms
- Reliability: 90 per cent to 99.99 per cent
LDPC (Low Density Parity Check) coding is used for data channels and polar coding is used for control channels.
Physical layer Sidelink Feedback channel (PSFCH) is used to reduce blind transmission and improve power efficiency.
Quality of Service in D2D communications is important, especially in V2X. Similar to 5G Quality Identifier (5QI), PC5 Quality identifiers are defined (PQI).
If the number of retransmissions is controlled, 5G NR Sidelink capacity will be more than that of LTE. If there is only one transmission (no retransmission), 5G NR SideLink will have twenty times the capacity of LTE Sidelink.
D2D in Release 17
Improvements continued in Release 17 covering Direct Discovery, Direct Communications, UE relays, enhanced power efficiency, enhanced reliability and Low Latency for 5G Proximity Services (especially public safety) in addition to V2X. Dynamic Spectrum Sharing supports coexistence of D2D with LTE/5G NR. Enhancements are supported to device discovery, relaying and power efficiency, also to NR Uu (Device to base station interface) and NR PC5 interoperability.
Way forward
D2D communication is an important aspect in 5G networks. 5G supports connectivity among a large number of devices. Growth in the number of devices requires a large number of spectrum resources to support a variety of applications and causes burden on the base station. D2D communication skips the need to forward data to the base station from the device and helps the devices to take part in direct peer to peer (P2P) transmission. It is expected that D2D will continue to evolve in future releases of the 3gpp standards.
(The author is a former Advisor, Department of Telecommunications (DoT), Government of India)

